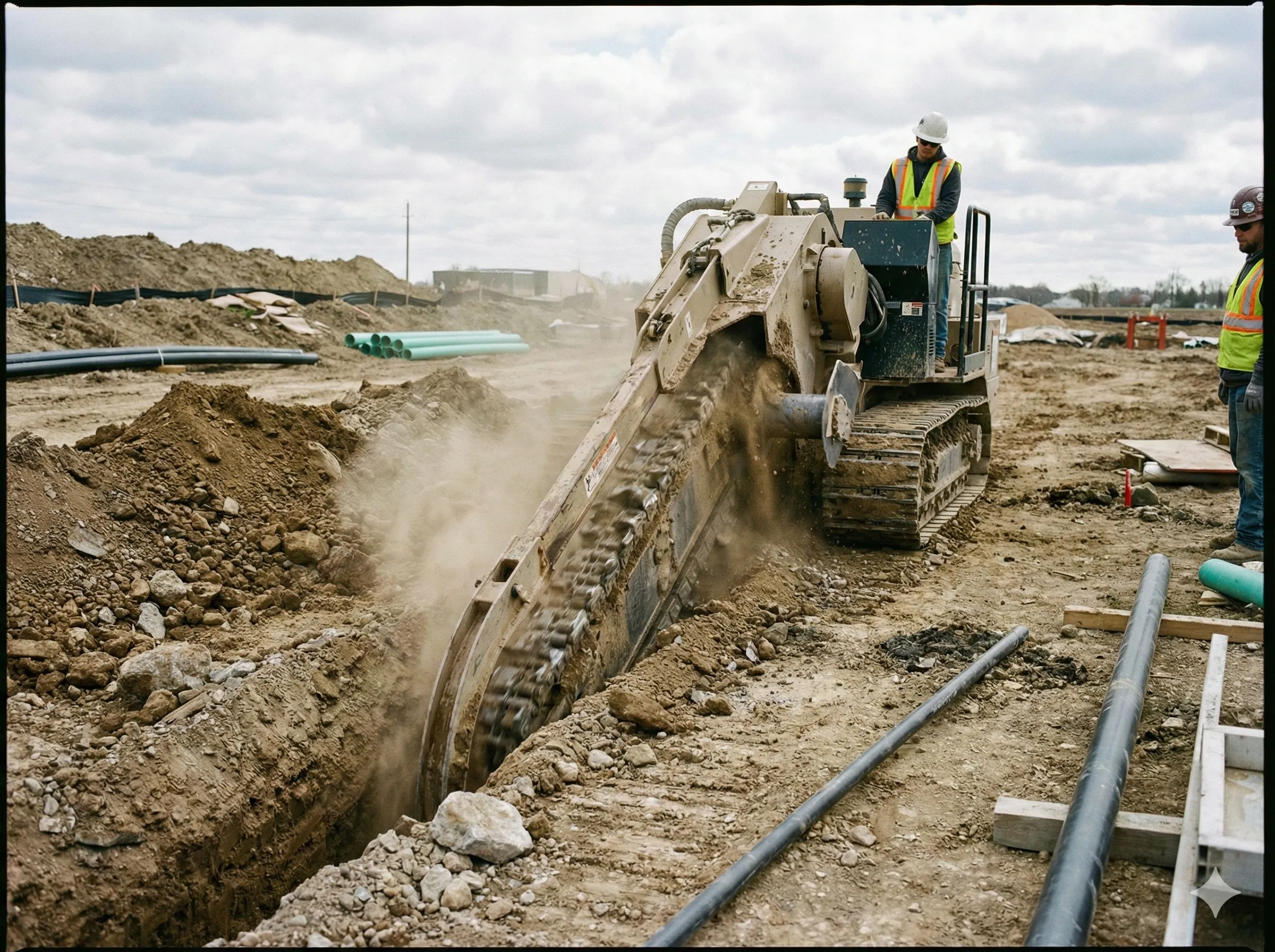
Railroad work is among the most demanding and dangerous occupations in the transportation industry. From repairing tracks and operating heavy machinery to maintaining electrical systems, rail workers face hazards every day. To prevent accidents and ensure safety, comprehensive protocols and strict federal regulations have been established. These measures not only safeguard workers but also help rail companies maintain operational efficiency and legal compliance.
The Importance of Track Safety in the Railroad Industry
Railway systems are complex networks that require precise coordination among personnel, machinery, and technology. Even a small oversight can lead to catastrophic consequences. Worker safety is, therefore, a cornerstone of railway operations. Federal agencies such as the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) enforce stringent standards for track maintenance, inspections, and worker conduct.
Ensuring adherence to these regulations is critical for minimizing workplace injuries, protecting lives, and upholding the integrity of the transportation system.
Common Hazards Faced by Railroad Workers
Railroad employees encounter a range of hazards daily. Understanding these risks helps establish more effective prevention protocols.
1. Track and Train Movement Hazards
One of the most significant dangers arises from trains and maintenance vehicles moving along the tracks. Workers must constantly stay alert to oncoming trains, as the noise from machinery can obscure warning signals.
2. Electrical and Mechanical Hazards
Workers who handle electrical systems or repair locomotives face electrocution and mechanical injury risks. Proper lockout/tagout procedures and protective gear are essential to minimize exposure.
3. Environmental and Weather Conditions
Extreme temperatures, rain, and icy tracks can increase the risk of slips, falls, and heat-related illnesses. Proper scheduling and weather-appropriate safety equipment mitigate these dangers.
4. Fatigue and Human Error
Long shifts and irregular work hours contribute to fatigue, reducing concentration and increasing the likelihood of accidents. Fatigue management programs and regulated work hours are crucial for safety.
Core Safety Protocols for Track Workers
Railway companies implement multiple layers of safety measures designed to reduce accidents and protect their workforce.
1. Training and Certification Programs
Comprehensive training is the first line of defense in preventing track-related injuries. Workers undergo mandatory instruction on hazard recognition, equipment operation, and emergency response. Recurrent training ensures employees remain updated on evolving safety standards and technologies.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE such as high-visibility clothing, helmets, gloves, safety boots, and hearing protection are required on all job sites. Reflective gear helps ensure workers remain visible, particularly in low-light or high-traffic conditions.
3. Flagging and Communication Protocols
Flagging systems and radio communications are vital for coordinating activities between train operators and maintenance crews. These systems alert workers to train movements and ensure teams clear the tracks in time. Standardized signals reduce miscommunication and human error.
4. Safe Work Zones
Temporary work zones with protective barriers or warning signals help isolate maintenance crews from active rail lines. These zones are clearly marked and monitored to prevent accidental entry by unauthorized personnel or trains.
5. Track Time Management
“Track time” refers to designated intervals when maintenance crews are allowed to occupy specific sections of track. Strict scheduling and coordination prevent multiple crews or trains from accessing the same track simultaneously.
Advanced Technologies Enhancing Railroad Safety
The integration of technology into railway operations has significantly improved worker safety. Automated systems, smart sensors, and predictive analytics now play key roles in identifying potential hazards before they escalate.
1. Drones and Remote Inspection Tools
Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can inspect tracks, bridges, and tunnels without requiring workers to physically enter hazardous areas. This reduces exposure to dangerous environments.
2. Wearable Safety Devices
Smart helmets and wearable sensors monitor a worker’s location, fatigue levels, and vital signs. Alerts are sent if the system detects excessive heat, fatigue, or proximity to moving trains.
3. Automated Warning Systems
Modern warning systems use motion sensors and GPS data to detect incoming trains and automatically alert nearby workers through lights, alarms, or vibration signals.
4. Predictive Maintenance Software
Machine learning algorithms analyze track data to predict when a section might fail or need repair. By addressing issues proactively, rail companies minimize the need for emergency repairs in dangerous conditions.
Emergency Response and Recovery Procedures
Even with the best precautions, accidents can occur. Swift and organized emergency response can make the difference between minor injuries and fatalities.
1. On-Site Emergency Kits and First Aid
All work zones are equipped with first aid kits and emergency supplies. Workers are trained in basic first aid, CPR, and how to respond to electrical or mechanical injuries.
2. Evacuation and Rescue Plans
Each work zone must have a defined evacuation route and rescue procedure. Regular drills ensure every team member knows their role during an emergency.
3. Reporting and Investigation
All incidents—no matter how minor—must be reported immediately. Investigations determine root causes and help prevent recurrence. Transparent reporting fosters accountability and continuous improvement.
Legal Protections and Rights Under FELA
Railroad workers in the United States are protected under the Federal Employers Liability Act (FELA), a law designed to provide compensation for injuries resulting from employer negligence. FELA ensures that workers who suffer injuries due to unsafe conditions, lack of training, or faulty equipment can pursue legal claims for damages.
To understand how FELA claims work and what rights injured workers have, see this resource: Railroad Worker Injuries and FELA Claims.
Promoting a Culture of Safety and Accountability
A strong safety culture starts with leadership. Employers must not only enforce safety rules but also encourage open communication and reporting without fear of retaliation. Safety audits, peer monitoring, and incentive programs further reinforce safe behaviors.
Role of Unions and Worker Advocacy
Labor unions play a critical role in advocating for improved safety standards and ensuring employers uphold their obligations. They collaborate with regulators and safety experts to propose better working conditions and training programs.
Role of Legal Support
In cases of workplace injury or employer negligence, workers may need professional legal representation. Firms experienced in FELA cases, such as Poolson Oden, provide essential support for employees seeking fair compensation and justice.
You can also learn more about the firm’s recognition in professional circles at Super Lawyers Profile.
Conclusion
Safety protocols for track workers are not static; they evolve with technology, regulations, and experience. Ongoing training, transparent reporting, and technological innovation remain at the heart of preventing injuries and fatalities.
Ultimately, safeguarding workers on the tracks is a collective effort—combining the responsibility of rail companies, government agencies, unions, and individual employees. When all parties uphold their roles, railroad work becomes not only more efficient but significantly safer for everyone involved.