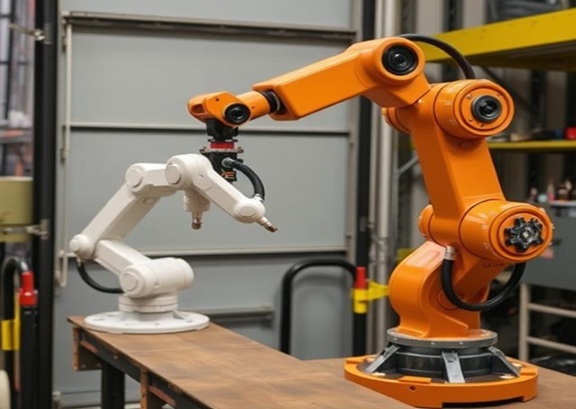
Manipulator arms are essential for executing various tasks, from industrial manufacturing to medical procedures. These devices are engineered to replicate the movements of a human arm, enabling machines to perform tasks that require precision, strength, and dexterity. Essentially, they serve as vital tools across multiple industries, enhancing both productivity and accuracy. Let’s delve into what a manipulator arm is, its applications, and the crucial component that works alongside it—the gripper.
The number one feature of a manipulator arm is to place, pass, or control objects with high precision, making them one of the best tool solutions for various industries that require accuracy and efficiency.
What Is a Manipulator Arm?
In simple terms, a manipulator arm is a robotic arm designed to interact with its environment. These robotic arms are equipped with joints, actuators, and various control mechanisms that allow them to perform movements similar to those of a human arm.
The basic structure of a manipulator arm includes:
Base: The foundation that supports the entire arm.
Joints: Connection points that facilitate movement, typically functioning either rotationally or linearly.
Actuators: Motors or hydraulic systems responsible for moving the joints and enabling the arm's motion.
End Effector: The device at the end of the arm used for tasks like gripping, welding, or lifting. This is where the gripper comes into play.
Manipulator arms come in various forms depending on their intended applications. Some are built for heavy-duty tasks such as welding or lifting in factories, while others are designed for delicate operations like surgery or assembling electronic components.
Uses of a Manipulator Arm
Manipulator arms have transformed numerous industries by automating complex, hazardous, or repetitive tasks. Common applications include:
Manufacturing and Assembly
In industrial environments, manipulator arms are frequently employed for assembly, welding, painting, packaging, and material handling. They can work tirelessly with precision, ensuring high-quality output. It Increases standard productivity and decreases the probability of human errors, making them an essential part of modern assembly systems.
Medical Applications
In healthcare, manipulator arms are utilized in robotic surgical systems such as the da Vinci Surgical System. These systems enable surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with enhanced precision and flexibility. The robotic arms can hold instruments, make precise incisions, or execute complex operations that may be challenging for human hands.Exploration and Hazardous Environments
Robotic manipulator arms are deployed in dangerous settings like space exploration and nuclear facilities. For example, they are used on space shuttles and stations to conduct repairs, perform experiments, or deploy satellites. Their ability to operate in hazardous environments without risking human lives is invaluable.Material Handling
In warehouses and distribution centers, manipulator arms automate the movement of goods from one location to another. This automation enhances operational efficiency and reduces labor costs by streamlining loading, unloading, and sorting processes.Robotic Simulation and Research
Manipulator arms play a crucial role in research and development within robotics and automation fields. They test new technologies and simulate human-like behavior in controlled environments by integrating sensors and cameras to mimic human hand movements under various scenarios.
The Gripper: An Essential Component
A pivotal aspect of a manipulator arm is the gripper. A gripper is a specialized end effector designed to grasp, manipulate, or release objects. Without a gripper, a manipulator arm would be limited to merely moving items; however, with one, it can interact with objects more intricately.
There are several types of grippers tailored for specific tasks:
Two-Finger Gripper: The most common type that mimics a human hand by pinching or grasping items.
Three-Finger Gripper: Offers three contact points for a more stable grip; often used in precision handling.
Vacuum Gripper: Utilizes suction to lift items; commonly found in packaging and material handling applications.
Magnetic Gripper: Employs magnetic forces to lift ferrous objects; ideal for industries dealing with metal components.
Soft Gripper: Made from flexible materials designed to handle delicate or irregularly shaped items without causing damage.
The choice of gripper largely depends on the nature of the object being manipulated, the required precision level, and the operating environment of the manipulator arm.
Conclusion
Manipulator arms have become indispensable tools in modern automation across various sectors—from manufacturing and assembly to surgery and exploration. Their versatility and precision make them ideal for handling repetitive, hazardous, or intricate tasks. A key feature of the manipulator arm is its gripper, which enables it to engage with the physical world by grasping, lifting, and moving objects in ways that closely resemble human hands.
Robotic manipulator fingers are utilized in dangerous environments, including space exploration, underwater exploration, and nuclear sites. For instance, robotic palms are used on area shuttles and space stations to carry out responsibilities like repairing systems, conducting experiments, or shooting satellites. Their capability to operate in dangerous, far-flung environments without risking human lifestyles is beneficial, much like how ergonomic material handling solutions ensure safety and efficiency in challenging environments on Earth.